- Find Faces → Discriminate between faces/non faces
- uses
- preprocessing step to Face Recognition
- Autofocus, Exposure, color balance in photography
- surveillance, biometrics, monitoring
- invariant to
- scale
- rotation
- illumination
Haar Features
a.k.a. Viola Jones Algorithm
slide windows of different scales across the image, extract features and classify the features as face/non-face
Haar Filters:
- Images are convolved with a set of Haar filters (24x24 base size) across different filter scales
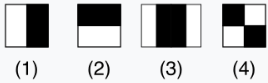
- Haar features are sensitive to direction of the filters
- The filters are themselves simple black and white (+1 and -1) filters
- the convolution can be simplified to simple summation

- filters are meant to capture certain facial features
Integral Image
- table that holds the inclusive sum of all pixel intensity values to the left and top of a given pixel
- 2D cumulative sum
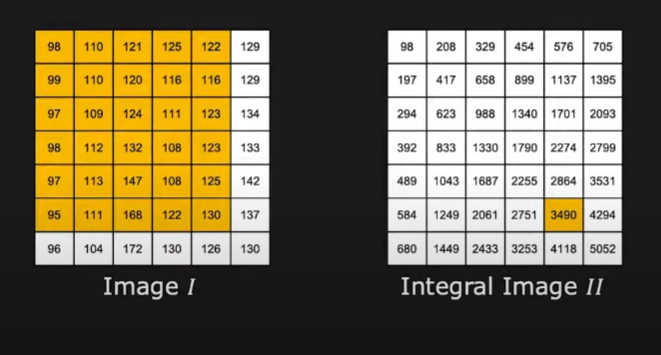
- integral images Allows for fast summation of image intensity of arbitrary rectangles
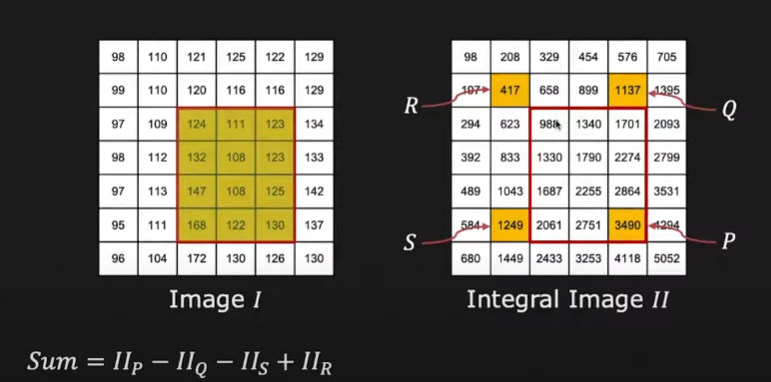
- Can be used to quickly compute Haar filters

- The computation cost remains constant regardless of the size of the Haar filter
Classification
- Haar features around a pixel need to be classified as face/non-face → Classification problem
- Nearest Neighbour Classifier
- large dataset needed for robustness
- slow and computationally expensive
- large dataset comparison
- have to do it for every scale
- Support Vector Classifier
- Nearest Neighbour Classifier
- Large number of features
- use Adaboost and Cascading to optimize classification
Adaboost
see Adaboost
- eliminate redundant/irrelevant features
- weak classifier: a relevant feature that does better than random guessing
- Adaboost constructs a strong classifier as a linear combination of weak classifiers
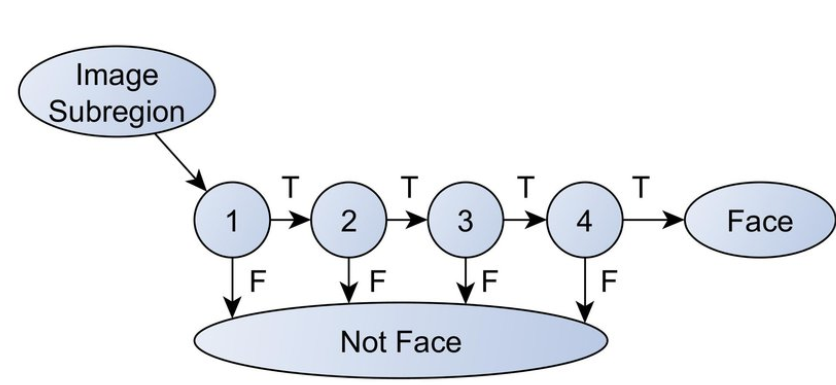
Cascading
- Strong features are formed into a binary classifier
- +ve matches are sent along to the next feature
- -ve matches are rejected
- Reduces the amount of computation time spent on false windows