- a.k.a. Linear Filtering
Similar to Rank Filtering
- a way to filter keeping the spatial pattern of pixels
- I’ = g * I
- where g is the kernel, I is the image and I’ is the convoluted image
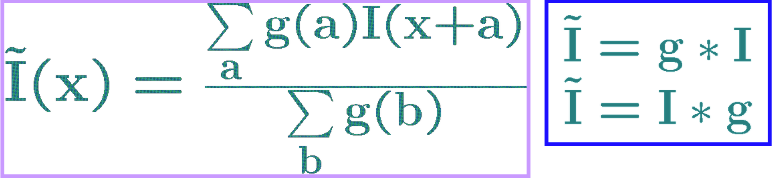
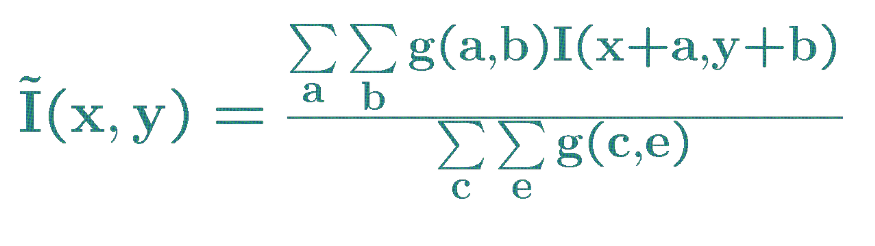 where g(a,b) is the kernel of size axb
where g(a,b) is the kernel of size axb- convolution is associative
Kernel/Mask/Filter Window
- The moving window
- common kernels
Decomposable Kernels
- symmetric kernels are decomposable into 2 linear convolutions
- if the kernel 2D matrix can be written as the outer product of 2 vectors
- n x n = n x 1 * 1 x n
- convolving with nxn kernel is the same as 2 convolutions with n x 1 and 1 x n kernels
- such convolutions are computationally cheaper
- 2n multiplications instead of n2 per pixel
Padding
- adding extra padding around the source image before convolution so that all the pixels in the source image get processed.
- Common padding techniques
- Zero: Set all pixels outside image course to zero
- Constant (border colour): set all pixels outside the source image to a specified border value
- Mirror: reflect pixels across the image edge