Method to find a camera’s internal and external parameters
Linear Camera Model - Forward Imaging Model
- mapping from 3D → 2D
- world coordinate frame (3D) → coordinate transformation to camera coordinate frame (3D) → perspective projection to image coordinates in the image frame (2D)
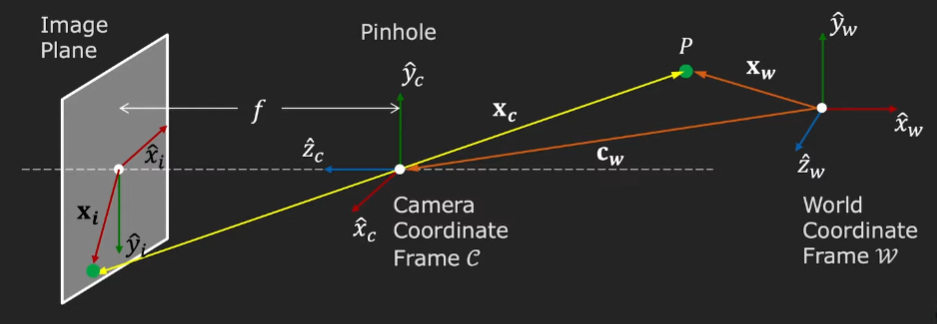
- World-to-camera transformation
- camera extrinsic parameters =
- rotation matrix
- translation vector
- combine to form an extrinsic matrix
- camera extrinsic parameters =
- Perspective Projection Equations
- from camera coordinate to image plane

- where u,v are the positions in the image, xc ,yc, zc are positions in camera coordinate frame
- camera intrinsic parameters =
- f is the effective focal length
- o is the principal point
- the equations are transformed into linear equations using homogenous coordinates resulting in an intrinsic matrix
- Projection matrix
- can combine extrinsic and intrinsic matrix into a single projection matrix
- using some image of a known real-world size of an object, it is possible to calculate this projection matrix
- the projection matrix can also be decomposed back into the extrinsic and intrinsic matrix