Corner: Point where 2 edges meet. i.e., rapid changes of image intensity in 2 directions
- Taking gradients
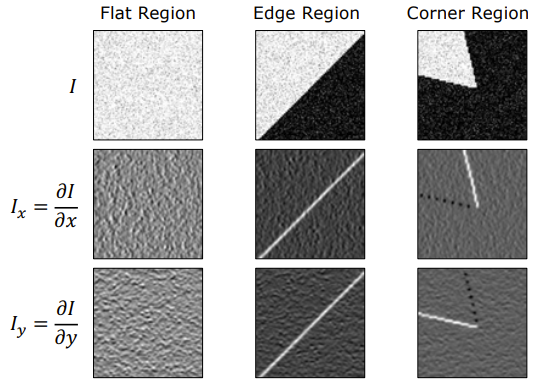
- distribution of gradients
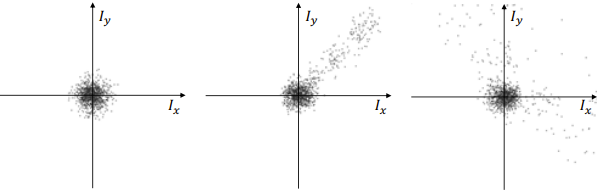
→ Classify the distribution of gradients to detect corners
- Moravec corner detector
- Harris Corner Detector
Harris Corner Detector
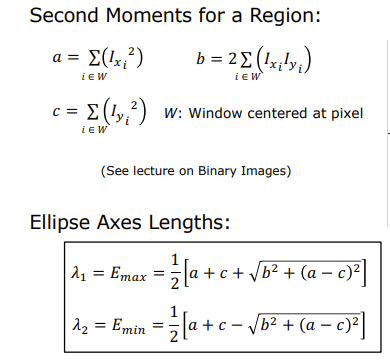
- Fitting an Ellipse to the distribution
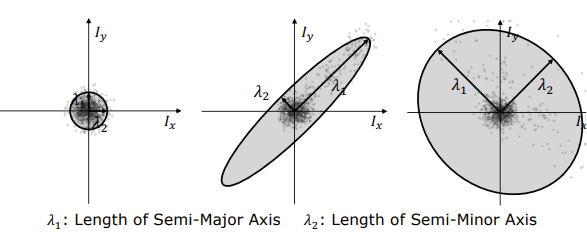
- the length of the axes become the parameters
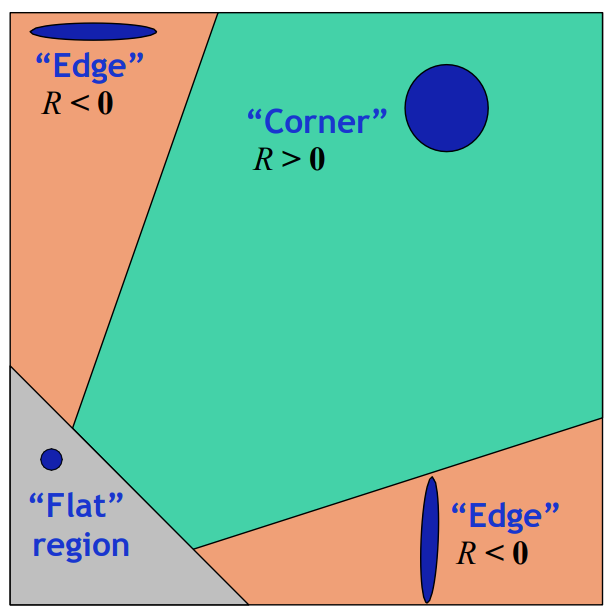
- if both axis are small → flat region
- if λ1 >> λ2 → edge region
- if both are large → corner region
- response function maps axis values to a number R
- R = λ1 λ2 - k (λ1 + λ2) 2
- where 0.04 ≤ k ≤ 0.06
- if R > threshold T → both axes are sufficiently large → Corner region
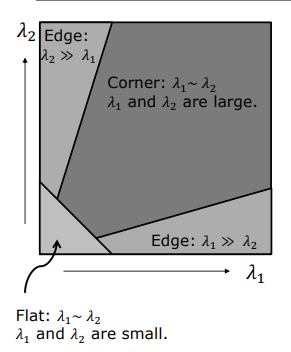
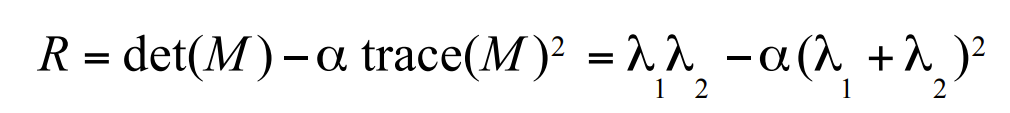
- response function maps axis values to a number R
- Finding axes values
- invariant to image rotation
- not scale invariant
- Use Harris-Laplace
- multiscale harris corner detection
- scale = Laplacian of Gaussian, approximated by Difference of Gaussians
- Use Harris-Laplace
Non-Maximal Suppression
- The detector is likely to produce large responses not only at the exact location of the feature but also close to it
- find the exact locations of the corners → detect the peak of each of these clusters → find local maximas
- Slide a window of size k over the image
- if the pixel at the center is the maximum value within the window, label it as positive (retain it).
- Else label it as negative (suppress it → reduced values, or eliminate it → set to 0)